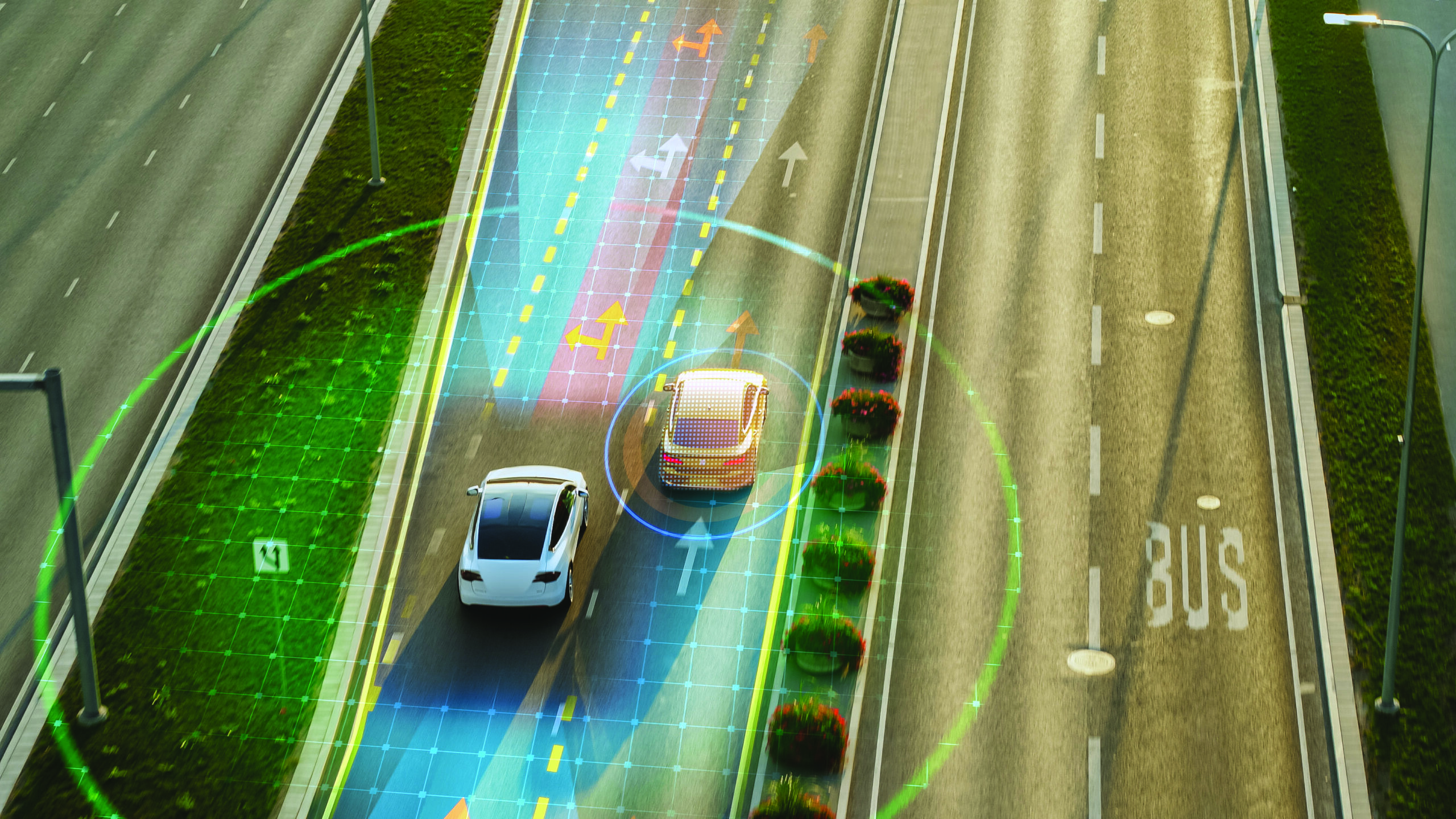
Self-driving cars, powered by sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI), promise to revolutionize transportation. These vehicles use complex algorithms, sensors and machine learning to navigate roads and avoid collisions. While the technology offers exciting potential—such as reduced traffic accidents and increased mobility—it also raises important questions about safety and liability when accidents occur. For personal injury attorneys and the public, understanding these issues is critical as the adoption of autonomous vehicles grows.
The Role of AI in Self-Driving Cars
AI in autonomous vehicles relies on a network of sensors, cameras and software systems to detect road conditions, interpret traffic laws and make split-second decisions. The ultimate goal is to minimize human error, which accounts for over 90% of traffic accidents. However, no technology is flawless, and self-driving cars are not immune to errors. Software glitches, hardware malfunctions or misinterpretation of sensor data can lead to accidents, posing significant safety risks.
For example, in recent years, there have been high-profile incidents involving autonomous vehicles. In some cases, these accidents were attributed to sensor failures that misread pedestrians or misinterpreted other vehicles’ movements. As a result, the safety claims of self-driving technology remain under scrutiny.
Liability in Self-Driving Car Accidents
When a self-driving car causes an accident, determining liability can be more complex than in traditional car crashes. In conventional accidents, liability often falls on the at-fault driver. However, in a self-driving car accident, multiple parties could share responsibility, including:
- The vehicle owner: If the car owner fails to maintain the vehicle or update its software, they might be partially liable.
- The manufacturer: If a design flaw or software error caused the accident, the car manufacturer could be held accountable under product liability laws.
- The software developer: If the AI system or algorithms malfunction, the software developer might share liability.
- Third-party vendors: Providers of specific components, such as sensors or cameras, may also be implicated if their products contributed to the failure.
Personal injury cases involving autonomous vehicles often require extensive investigation to identify the root cause of the accident and the responsible party. This may involve reviewing the car’s data logs, examining software performance, and consulting with AI and automotive experts.
The Rise of Ride-Sharing Driverless Cars
The introduction of autonomous vehicles into the ride-sharing market adds another layer of complexity to safety and liability concerns. Companies like Waymo, Cruise and Amazon’s Zoox are at the forefront of deploying self-driving cars for public transportation.
Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet, is a leader in robotaxi services and boasts a strong safety record compared to some competitors. For instance, Cruise, a driverless taxi service owned by General Motors, had its California license suspended following a serious incident in which one of its vehicles dragged a pedestrian in San Francisco. Despite this setback, Cruise is attempting to rebound by partnering with Uber to relaunch its services in U.S. cities by 2025.
Waymo has also aligned with Uber, announcing plans to expand its operations to Atlanta and Austin, Texas, next year. Meanwhile, Amazon’s Zoox is positioning itself as another major player, aiming to launch public driverless rides in Las Vegas by 2025, with an expansion to San Francisco soon after.
For passengers and pedestrians, these advancements in ride-sharing services highlight the importance of robust safety protocols and transparency. When accidents occur, liability may involve not just the ride-sharing company but also the technology developers, manufacturers and even the platforms facilitating these services.
How Personal Injury Law is Evolving
As self-driving technology advances, laws governing liability in autonomous vehicle accidents are also evolving. Many jurisdictions are still in the process of drafting regulations to address these unique challenges. For example, some states have introduced legislation requiring autonomous vehicle manufacturers to carry special insurance policies or assume full liability when their cars are in autonomous mode.
For personal injury attorneys, these developments highlight the importance of staying informed about emerging technologies and legal precedents. Attorneys must be prepared to navigate the technical complexities of AI systems and work with experts to build compelling cases for their clients.
Staying Safe with Autonomous Vehicles
The rise of self-driving cars and ride-sharing services marks a significant shift in transportation, offering both promise and potential risks. While autonomous vehicles have the potential to reduce accidents, users should approach the technology cautiously by staying informed, updating software regularly and understanding the vehicles’ limitations. For those injured in accidents involving this emerging technology, understanding liability is critical to seeking fair compensation.







Leave A Comment